Lab2 data types and arithmetic operators(done 缺少c和c++都有自己的一套标准输入输出解释部分)
C++ Formatting with cout
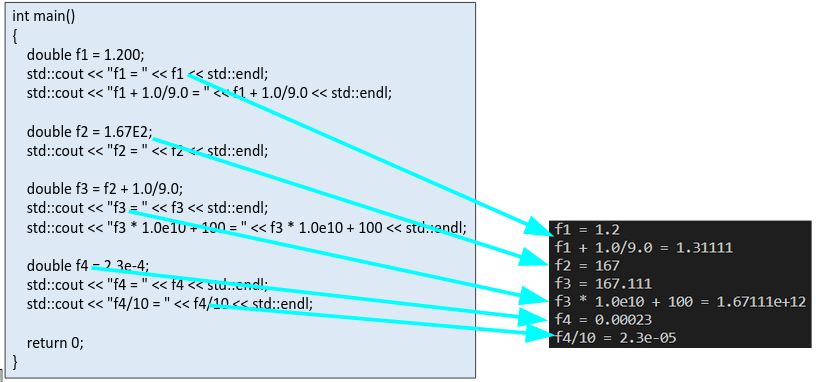
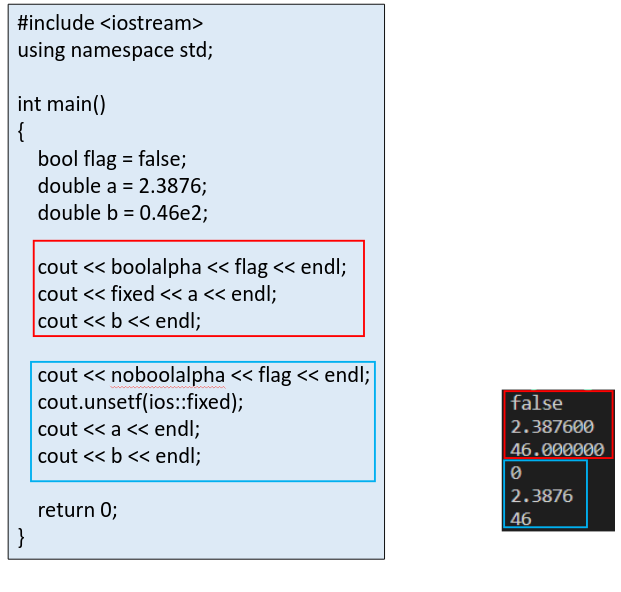
Floating-point types are displayed with a total of six digits, except that trailing zeros(尾随零) aren’t displayed.
The float number is displayed in fixed-point notation or else in E notation depending on the value of the number. In particular, E notation is used if the exponent is 6 or larger or -5 or smaller.
下面是一个例子
C++ provides two methods to control the output formats
Using member functions of ios class
第一个原型cout.set(fmtflags):

举例来说
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
bool flag = true;
// 使用 setf 设置 boolalpha 标志,显示布尔值为 true/false
cout.setfboolalpha;
cout << "Boolean: " << flag << endl; // 输出 "true"
// 设置十六进制格式
int num = 255;
cout.setfhex;
cout << "Hexadecimal: " << num << endl; // 输出 "ff"
return 0;
}
输出
Boolean: true
Hexadecimal: ff
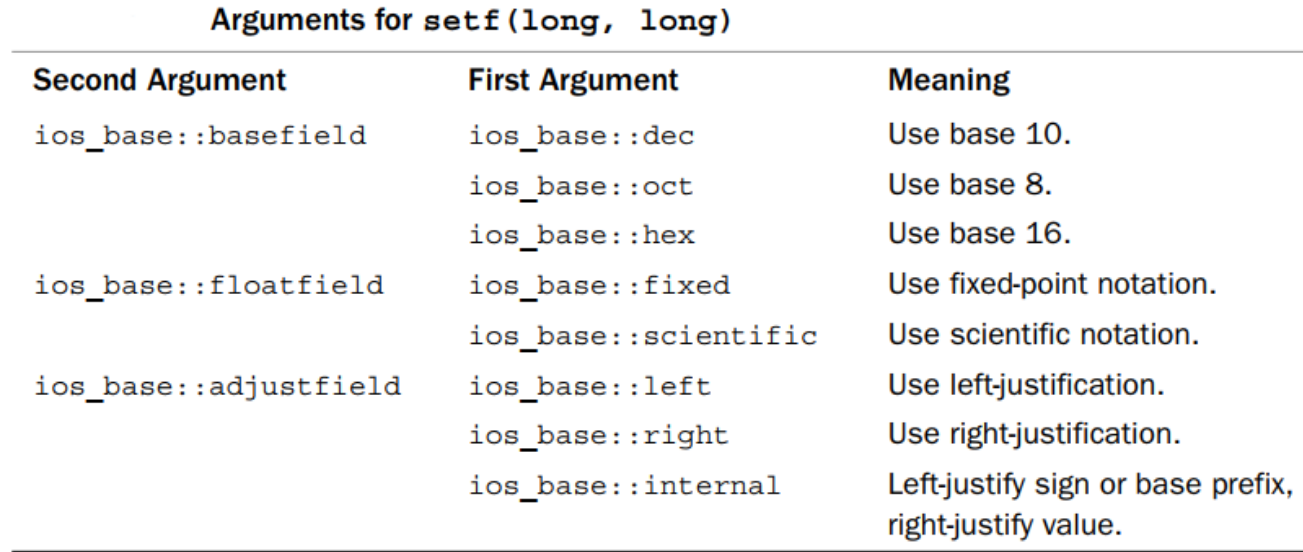
第二个原型cout.set(fmtflags,fmtflags):注意两个参数及其对应。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
double pi = 3.141592653589793;
// 使用双参数版本,改变浮点数格式为科学计数法
cout.setfscientific, ios::floatfield;
cout << "Scientific: " << pi << endl;
// 将浮点数格式设置为固定小数点形式
cout.setffixed, ios::floatfield;
cout << "Fixed: " << pi << endl;
return 0;
}
结果:
Scientific: 3.141593e+00
Fixed: 3.141593
解释:
ios::floatfield是一个掩码,它代表与浮点数表示相关的所有标志(包括ios::fixed和ios::scientific),因此这行代码不会影响其他的格式标志(比如进制表示方式)。- 同样地,当我们调用
cout.setffixed, ios::floatfield时,固定小数点格式会替换科学计数法。
两种对比
- 单参数版本会直接设置标志,并且可能影响所有的格式标志。
- 双参数版本通过掩码来控制哪些特定标志位被更改,提供了更精细的控制。
更多的ios class成员
cout.width(len) //set the field width
cout.fill(ch)//fill character to be used with justified field
cout.precision(p)//set the precision of floating-point numbers
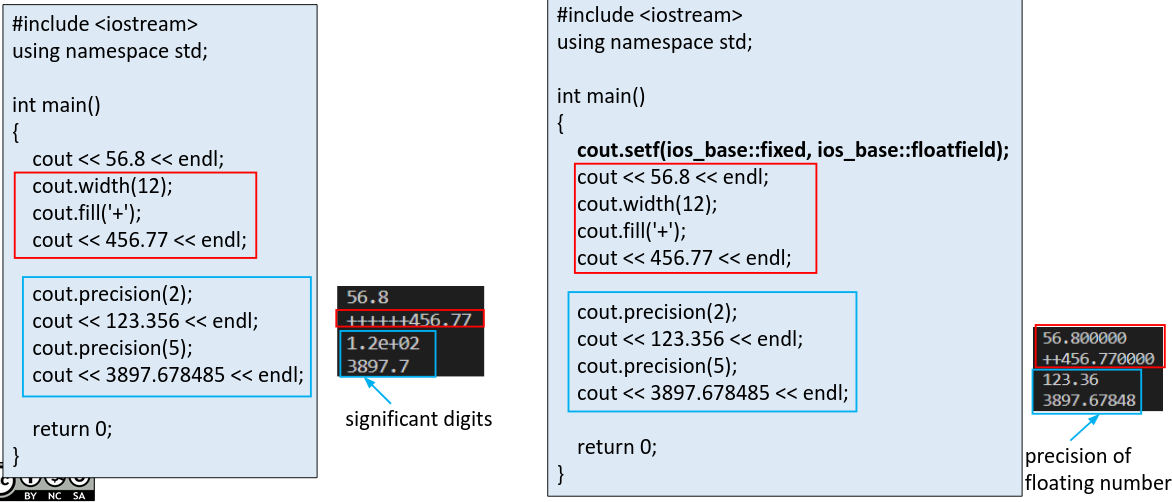
效果解除
The effect of calling setf() can be undone with unsef()

Using iomanip manipulators
#include <iomanip>
我们有一些操作符也能完成上面的效果。
例如下面的这些
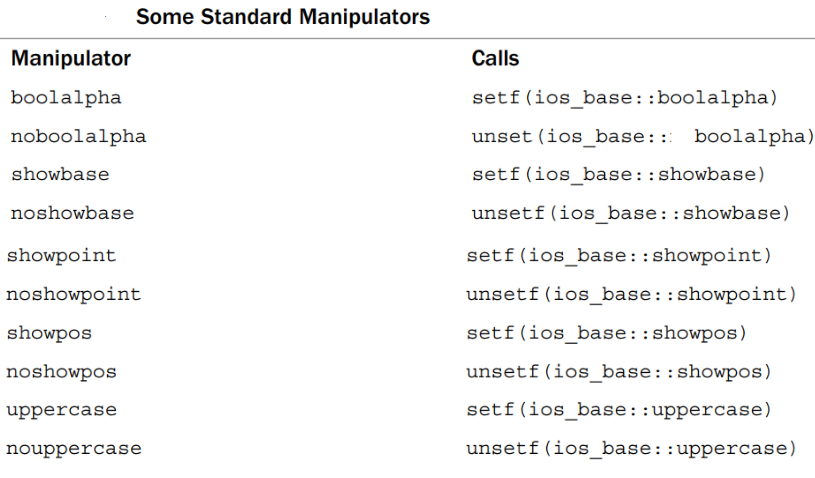

使用的例子如下
更多
setw(p):- 用于设置输出字段的宽度为
p个字符。如果输出的内容不足p个字符,系统会根据设置的填充字符填充空白区域。
- 用于设置输出字段的宽度为
setfill(ch):- 用于设置填充字符,
ch是你想要使用的字符。这个填充字符会在输出宽度不足时,用于填充空白区域。
- 用于设置填充字符,
setprecision(d):- 用于设置浮点数的小数位数精度为
d。这会影响后续浮点数的输出格式,通常和std::fixed或std::scientific一起使用,以决定输出的具体格式。
- 用于设置浮点数的小数位数精度为

对比
Exercise
1

结果
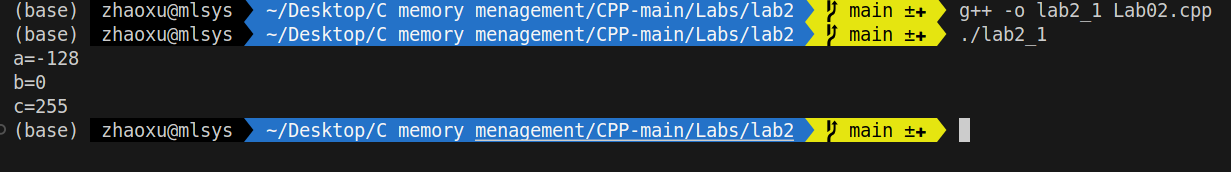
a: 我们定义了一个有符号char,实际上,最多能存127,但是我们让他自增了一个,相当于01111111变成了10000000,正好是最大的负数。
b:是一个无符号的char,代表最大的二进制数,就是11111111,++后直接变成00000000
c:同b,从00000000变成了11111111.
2
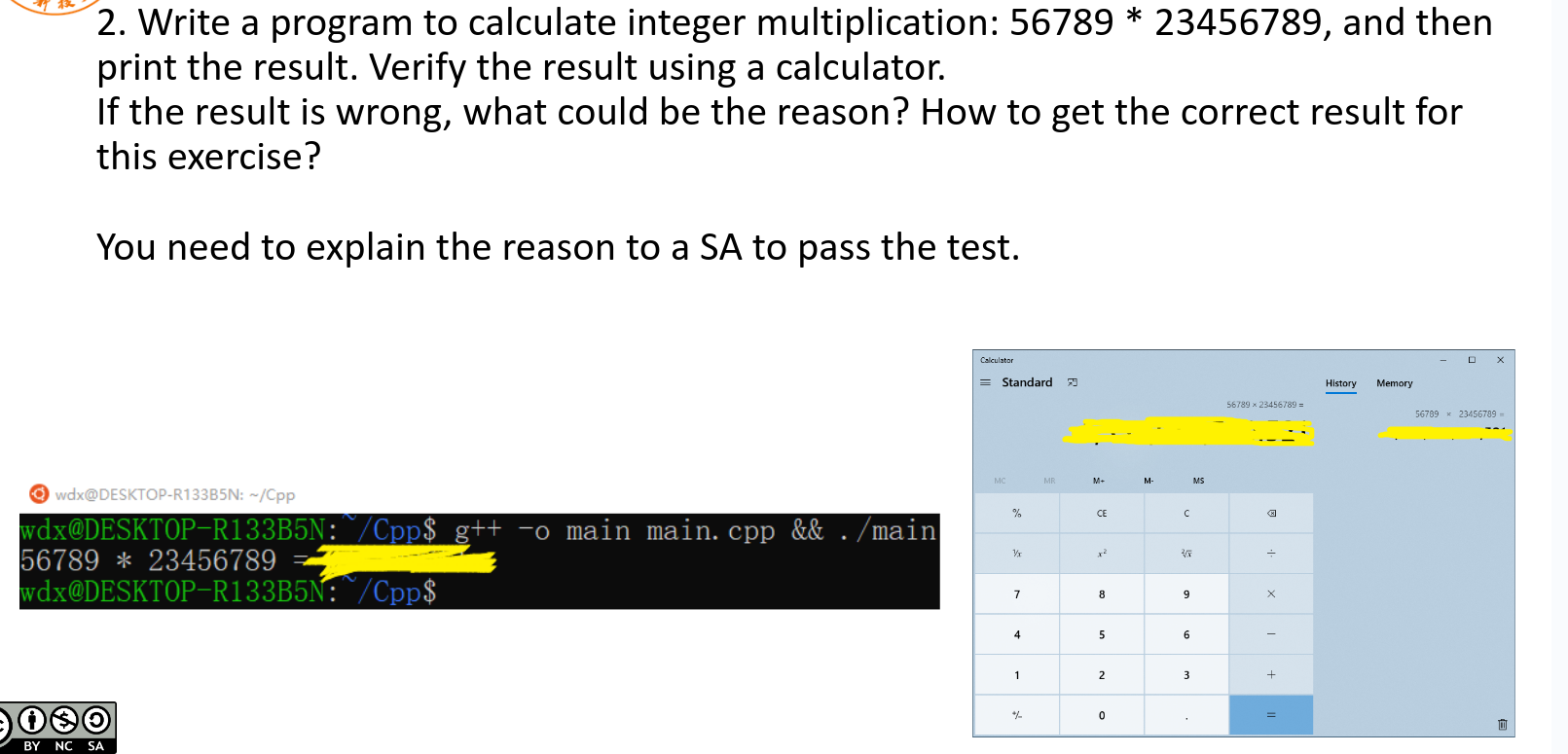
结果没问题。

3


是这样的,浮点是其实是采样,第二个虽然是0.1但是存在变量中的真实数字是有一个小误差的,这个误差累加十次仍然不能在有限的精度下看出来,因此跟1.0f不相等。
我们看一下是不是这样。

果然如此,就是不一样的。
4

g++ -o lab2_4 lab2_4.cpp -w
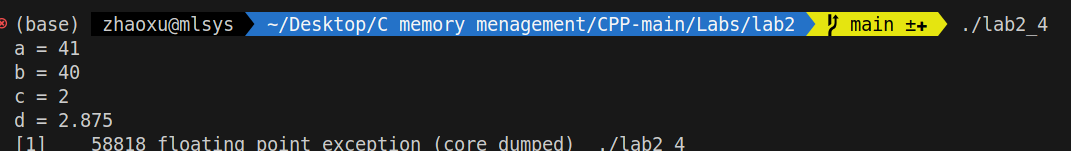
a是因为41.98,但是赋值给a的时候,a是一个int,发生了强制类型转换,小数部分失踪,第二个b是因为直接进行类型转换相当于19加上21,c是因为右边的两个数全是int类,因此结果自动也是int类型,保留整数部分,最后一个是因为有一个double类型,右边最后是double。
5

结果是30.
很正常,因为auto在第一步中就变成了int类型,第二步其实是double的常量强制转换为int,第三步是一个int和一个double相加,计算过程中两者全部变成double,但是最后发生强制类型转换成int,因此是30